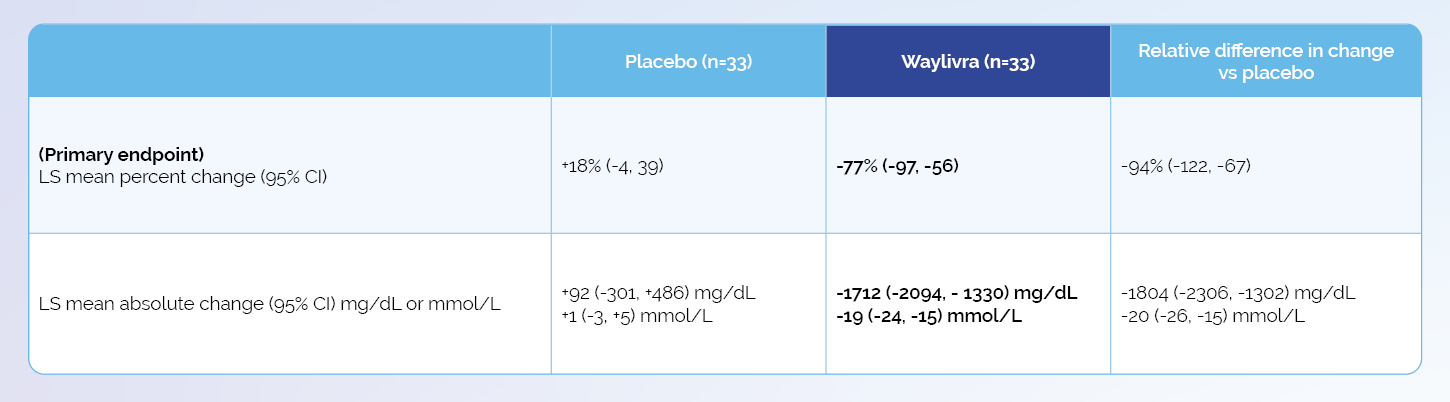
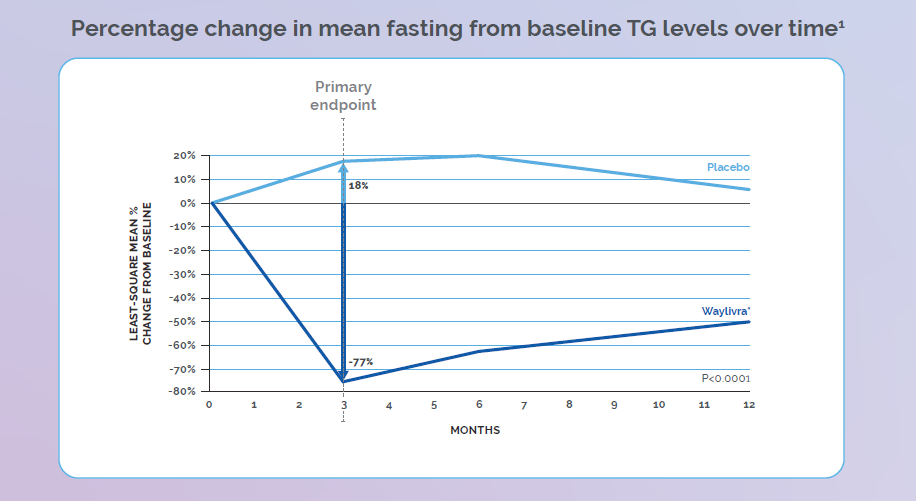
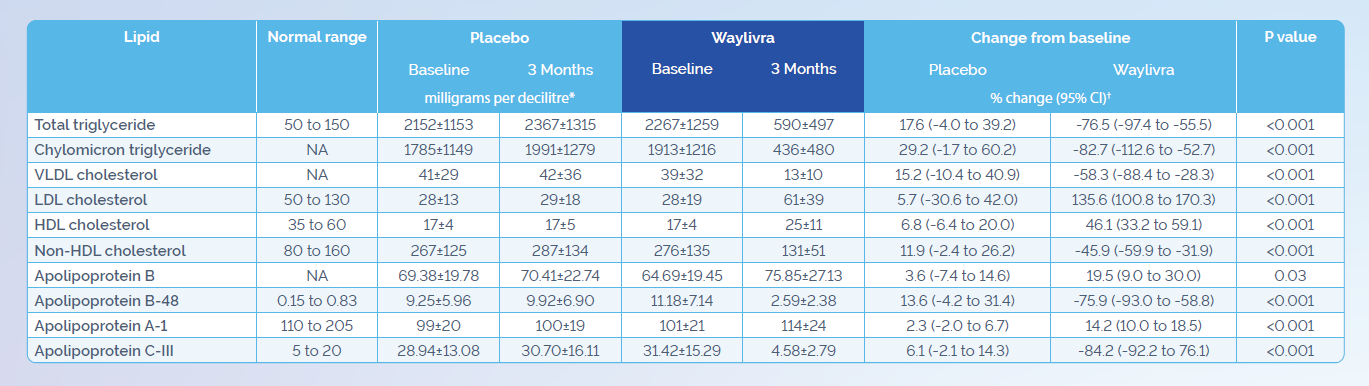
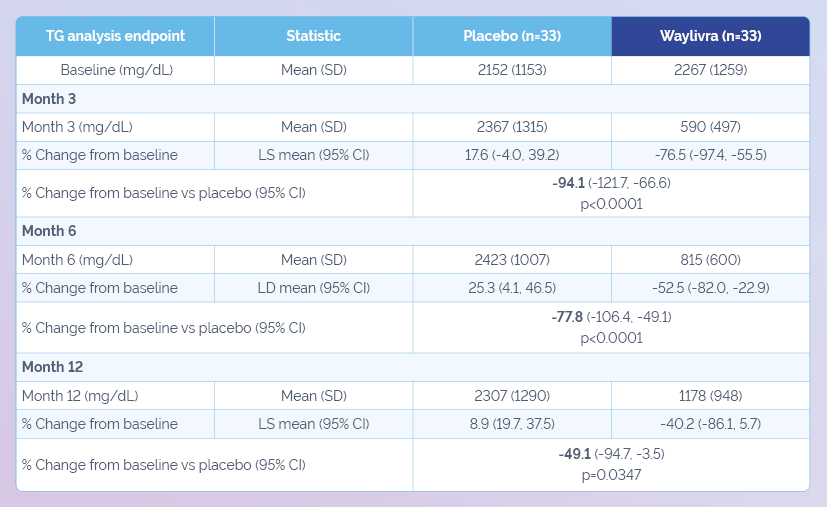
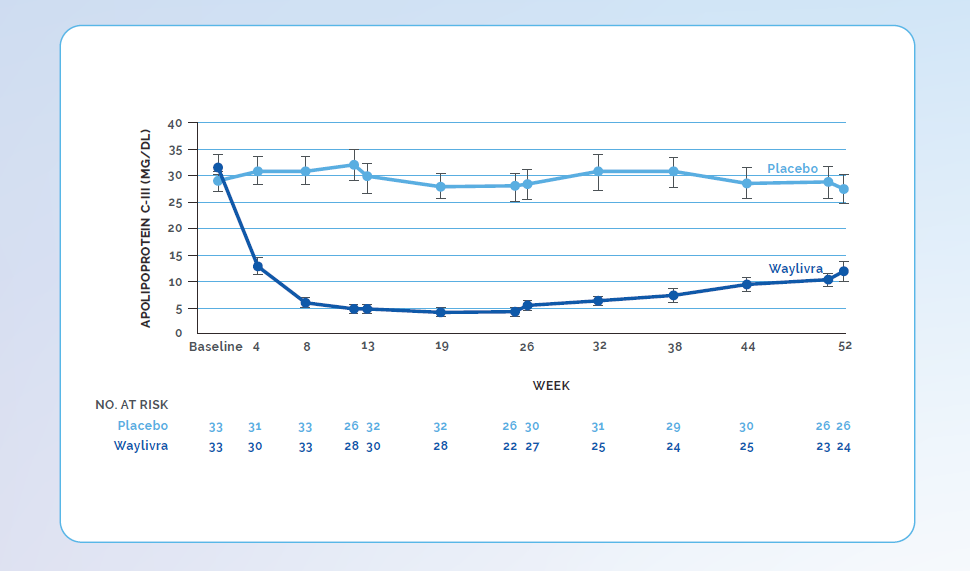
Adapted from Witzum JL et al. N Engl J Med 2019;381(6):531–42.
* Plus-minus values are means ±SD. To convert the values for TG to millimoles per litre, multiply by 0.01129. CI denotes confidence interval, HDL high-density lipoprotein, LDL low-density lipoprotein, NA not available, and VLDL very low-density lipoprotein.
† The values are least-squares means. The least-squares means values, corresponding 95% confidence intervals, and P values are derived from analysis of covariance models, with percentage change from baseline as the dependent variable; treatment group, presence or absence of pancreatitis, and receipt or no receipt of concurrent n−3 fatty acids, fibrates, or both as factors; and log-transformed baseline TG levels as a covariate.
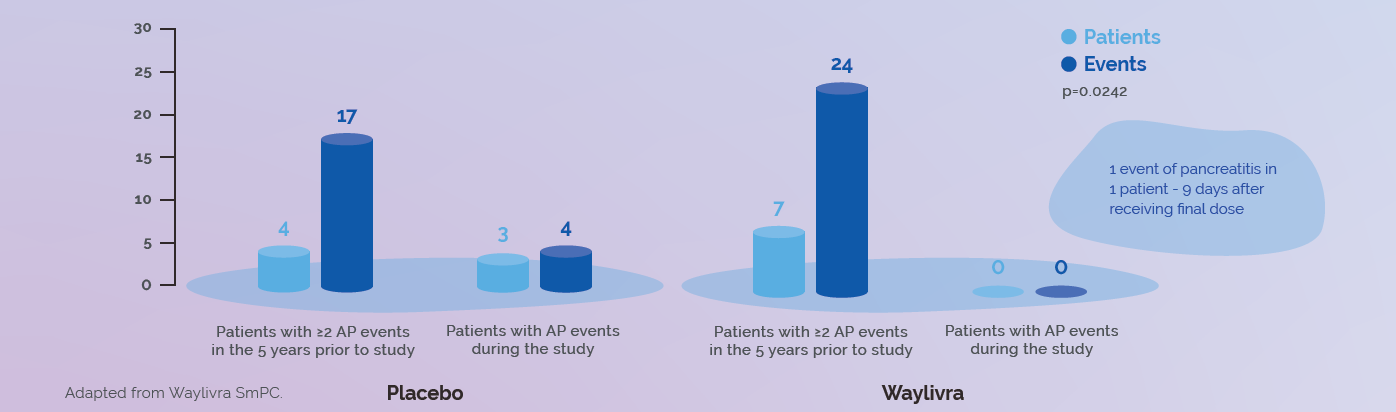
A post hoc analysis of patients with a history of recurrent pancreatitis events (≥2 events in the 5 years prior to Study Day 1) showed a significant reduction in pancreatitis attacks in Waylivra-treated patients compared to placebo-treated patients (p=0.0242).1
Pancreatitis attacks* during the 52-week study period
• in the Waylivra group: none of the 7 patients who had 24 pancreatitis attacks* in the 5 years prior to study enrolment experienced an attack
• in the placebo group: 3 of the 4 patients who had 17 pancreatitis attacks* in the prior 5 years experienced 4 attacks1,2
▼ This medicinal product is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions. Adverse events should be reported. Reporting forms and information can be found at www.mhra.gov.uk/yellowcard. Adverse events should also be reported to Swedish Orphan Biovitrum Ltd at [email protected] or Telephone +44 (0) 800 111 4754