Aspaveli is indicated as monotherapy in the treatment of adult patients with paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria (PNH) who have haemolytic anaemia.1
Improvements in fatigue
See improvements in fatigue at Week 16
At Week 16, patients achieved clinically meaningful improvements in fatigue:‡§2
Due to hierarchical testing, the change from baseline in FACIT-Fatigue score was not tested for non-inferiority.
+9.2-point
mean change in FACIT-Fatigue score from baseline with Aspaveli vs -2.7 points with eculizumab (total mean difference: 11.9 points)
73%
of patients receiving Aspaveli achieved clinically meaningful improvements in fatigue vs 0% of patients receiving eculizumab
See sustained improvements in fatigue through Week 48
Through Week 48, clinically meaningful improvements in fatigue were sustained.‡3
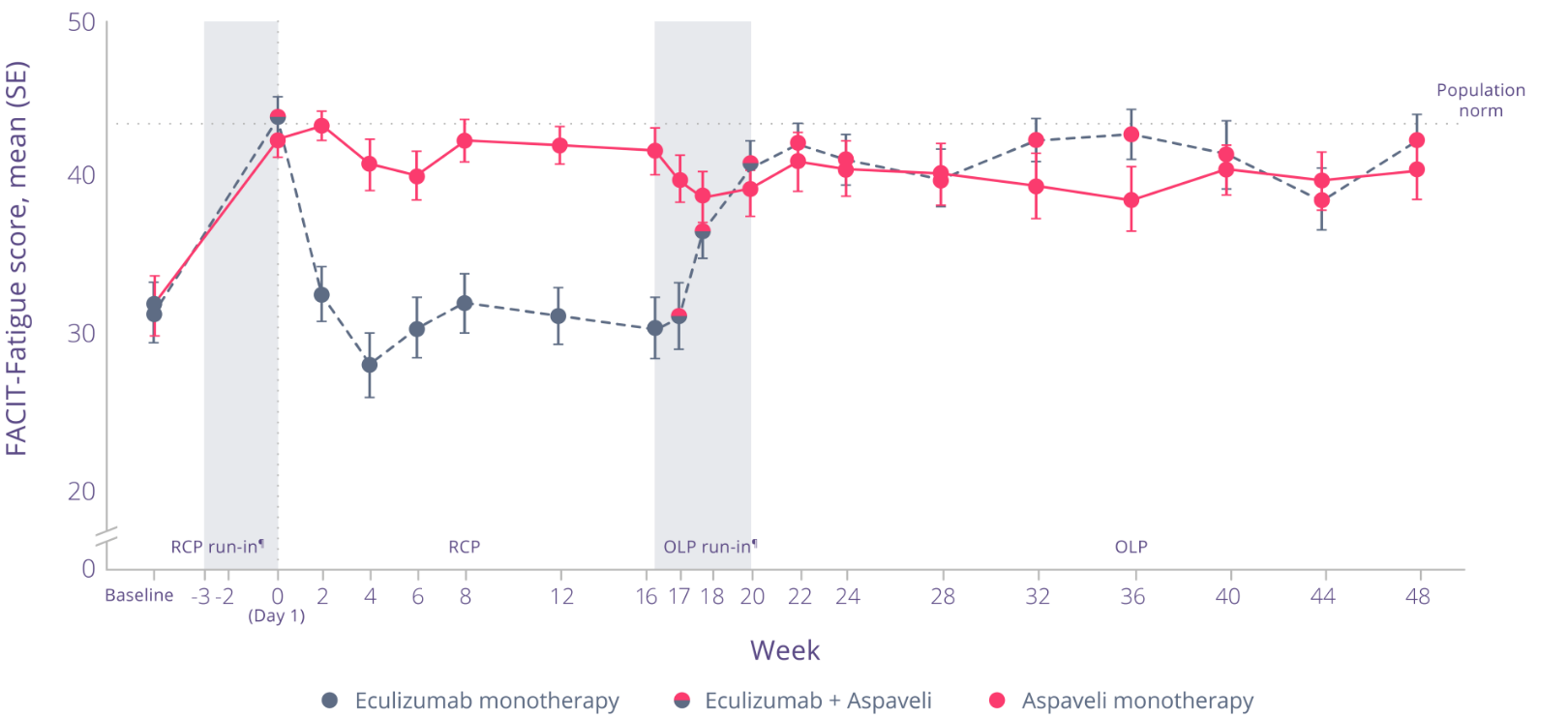
Adapted from Peffault de Latour R et al. Lancet Haematol. 2022.
Through Week 48:3
- Patients who continued to receive Aspaveli maintained clinically meaningful improvements in fatigue‡
- Patients who switched from eculizumab to Aspaveli at Week 16 achieved significant improvements in fatigue (P<0.0001)
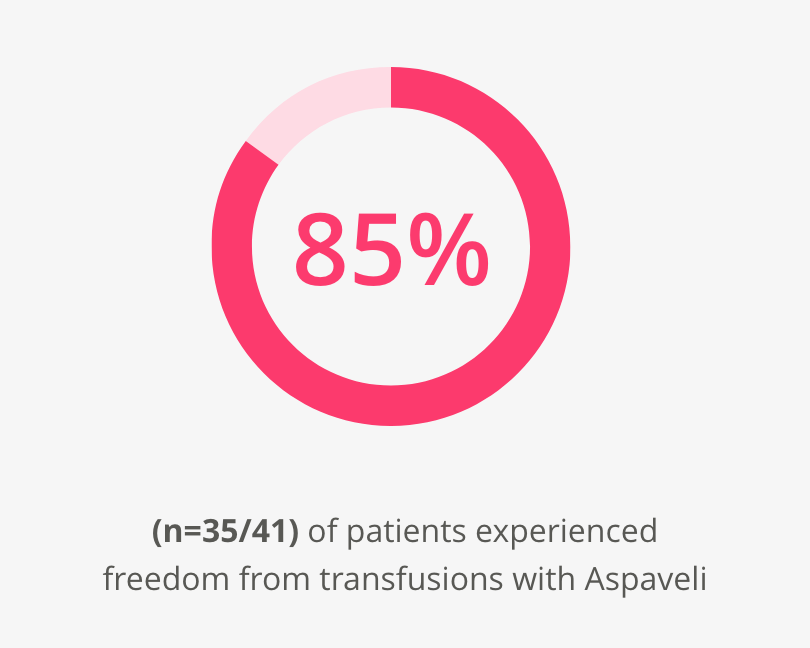
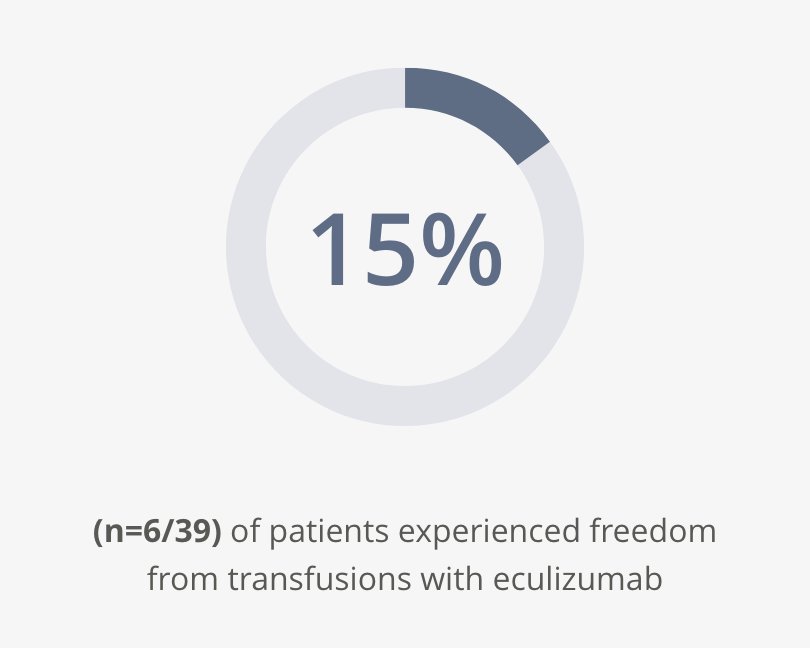
Transfusion independence
Aspaveli reduces the burden of transfusions.2,3
At Week 16:2
At Week 48:3

>70% of both patients who continued to receive Aspaveli (n=30/41) and patients who switched from eculizumab to Aspaveli at Week 16 (n=28/39) were transfusion-free
‡A ≥3-point change in FACIT-Fatigue score is considered to be clinically meaningful.2
§This difference was considered to be clinically significant, but non-inferiority was not assessed because of the pre-specified statistical hierarchical testing rules. 73% of patients in the Aspaveli group had at least a 3-point increase in FACIT-Fatigue scores at Week 16, as compared with 0% in the eculizumab group; a 3-point change is considered clinically significant.1,4